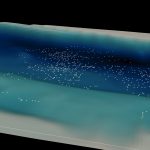
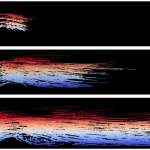
 The computation of the wind at small scale and the estimation of its uncertainties is of particular importance for applications such as wind energy resource estimation.
The computation of the wind at small scale and the estimation of its uncertainties is of particular importance for applications such as wind energy resource estimation.
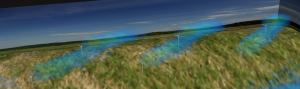
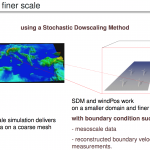
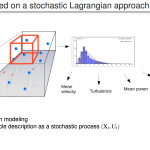
To this aim, we develop a new numerical method based on the combination of an coarse prediction (based on Numerical Weather Prediction model) or statistical wind behaviors (based on measurement campaign and local observations) and a Lagrangian Stochastic Model, adopting a fully Lagrangian viewpoint for the turbulent flow modeling in the atmospheric boundary layer in order to refine the simulation in the computational domain.
SDM-WindPoS is a model for the simulation of wind in the atmospheric boundary layer.
SDM-WindPoS uses a Lagrangian approach to solve the dynamical equations of the wind. Based on a turbulent-fluid-particle model description, SDM-WindPoS is an advantageous alternative for some application domains, such as dynamical downscaling simulations and wind farm simulations.
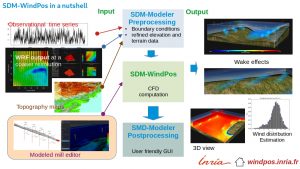
SDM-WindPoS is currently made of several blocks:
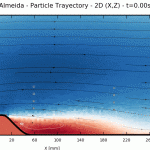
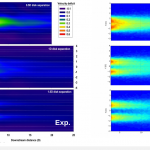
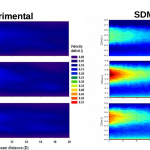
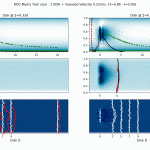
- Its numerical kernel, SDM-kernel. The stochastic downscaling method (SDM) adopts the viewpoint of a fluid-particle dynamics in a flow. Such numerical methods are computationally inexpensive when one need to refine the spatial scale. This is a main advantage of the SDM approach, as fluid-particles methods are free of numerical constraints. SDM involves various simulation techniques whose combination is totally new (such as Poisson solvers, optimal transportation mass algorithm, original Euler scheme for confined Langevin stochastic processes, and stochastic particle methods). Turbulence modeling inside SDM follows the main framework of fluid particle modeling in turbulence.
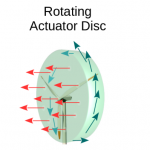
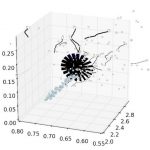
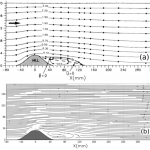
- WindPoS-LAM, the package for the simulation of wind mills (LAM holds for Lagrangian Actuator Model). This package performs a Lagrangian computation of the classical actuator disk (AD) method (non rotating, rotating, BEM like), according to the spacial discretization situation (size of the farm, single wind turbine and wind tunnel case).
- WindPoS-ATMOS, is a library that contains the specific computational models used in SDM for simulations in the atmospheric boundary layer.
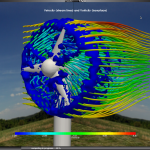
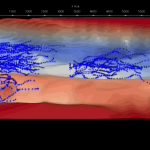
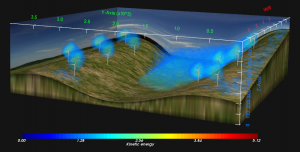
- SDM-Modeler, the dedicated SDM graphic user interface for the pre- and post-processing of SDM simulations and its specialized libraries. Modeler helps to configure the execution of a simulation, and assist in its configuration. It allows to visualize, compare, the 3D views of all SDM simulation outputs, including the interaction rendering with the wind turbines of the LAM part.
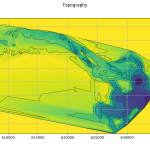
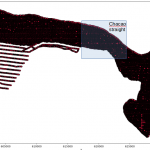
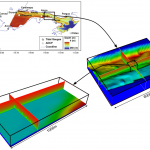
Modeler also visualizes and imports WRF weather forecast data and topographic data, to extract initial and boundary conditions for a finer mesh simulation.
Summary of current and part projects